KP-F1A HVDC Control Protection Simulation Device

HVDC transmission is widely used in power system, especially the long distance and large capacity transmission, and the mutual influence of AC system and DC system or multiple DC system has become a hot research topic in power system. To carry out this research, it is bound to establish a corresponding simulation system, which is the core part of this simulation system.
Power system simulation is divided into Non Real Time Simulation and Real Time Simulation. Due to the low efficiency of the Non Real Time Simulation, it can not access the actual device, so it is widely used in the field of engineering application and system research, and the RTDS Real Time Simulation technology is widely used in power system simulation.

RTDS provides a rich model library, which can easily finish a simulation modeling of AC or DC primary system. The protection of its own control model of HVDC control model can build the foundation, but because its control characteristics have a large deviation with the actual, that can not meet the actual application requirements. Therefore, it can only use the actual HVDC control and protection device the way.
Although actual device access mode has solved the bottleneck problem of HVDC transmission system, however, this way also has the problems with high cost, large workload, low efficiency and long period. Even if the equipment is only one, it has to be joined up into all the control and protection devices of the whole project which generally tend to have more than 100 cabinets, therefore, it is very difficult to achieve for the general users.
KP-F1A provides a new model for the simulation of HVDC control protection. Based on the source program of actual control to build a entirely consistent simulation program, and using a high-speed fiber channel to achieve the closed-loop control for RTDS simulation, which is at low cost, high efficiency, high reliability, makes it possible for the general users to do the HVDC system simulation.

Pole Control System
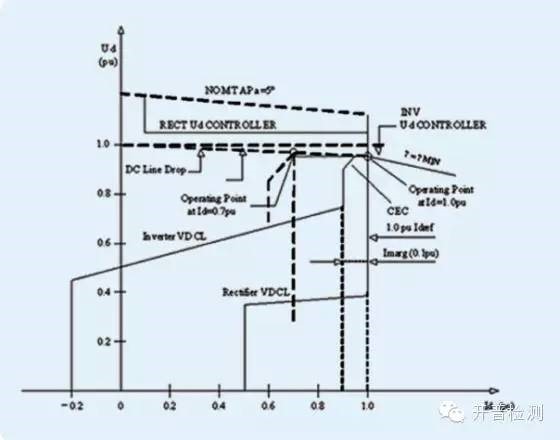
Pole control system contains a dozen control units (including dc power/current control, transient stability control, current balance control, current margin compensation control, inter electrode power transfer control, overload control, transformer tapping control, constant DC current control, constant dc voltage control, constant extinction angle control, etc.). Control units cooperate with each other, and under different operation conditions, there are different input modes and combination patterns. The operating characteristics of the HVDC system is mainly controlled by the dc voltage regulator, dc current regulator, and extinction angleregulator.
DC CURRENT CONTROL
Determination of Current reference
Current margin compensation
Voltage dependent current limit control
Transient current control
The inter electrode power transfer
Current balance control
Group voltage balance control (EHV)
Deblock sequence (EHV)
Series valve group deblock/block (EHV)
DC PROTECTION
In a system failure or other abnormal conditions, the DC protection by electrical detection of corresponding (current, voltage, power, frequency, etc.) changes or other non electrical quantity, make the correct response, and prevent damage to the HVDC equipment safe and stable operation of HVDC transmission system.
DC Converter Protection
Valve short circuit protection
Commutation failure protection
Twelve-pulse bridge differential current protection
Valve differential DC current protection
DC LINR PROTECTION
DC travelling wave protection
DC voltage sensing protection
Low-voltage of DC transmission line protection
Longitudinal differential protection of DC transmission line
Transverse differential protection of DC transmission line
Restart of DC transmission line
STATION CONTROL SYSTEM
The station control system mainly includes the AC filter and converter transformer tapping control.
AC Filter Control
Minimum filter
Reactive power control
AC voltage control
Dead-time control
Converter Transformer Tapping Control
Reactive power control
AC voltage control
Dead-time control
- 上一篇:KP-F6 Multi-function Recorder 2014/12/9
- 下一篇:KP-F8 RTDS Automatic Test Syst 2014/12/8


